

Robots may be distinguished between stationary machines which usually perform tasks through actuator arms and mobile robots which move can locomote, that is, move to different locations and may be smart enough to walk around, over or under barriers. Stationary robots may be employed on assembly lines. Mobile robots might be used to explore a remote surface such as another planet.
Examples of both are shown below.
The first row shows some stationary robots. Each is anchored to a fixed location. The actuator arms perform repetitive tasks like placing parts, spot-welding or painting.
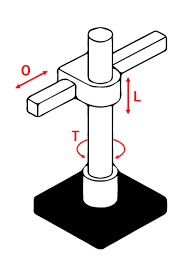
Their motion may be translational along three linear axes, x, y, z, or two linear axes x, y with a cylindrical axis, as illustrated for the left-most robot in the top row.
Their motion may be spherical along orthogonal rotational axes azimuth and elevation in combination with a translational axis which may be horizontal or vertical.
They may have SCARA ("selective compliance assembly") motion which is often used for pick-and-place operations.
They may have articulated motion.
 |
 |
 |
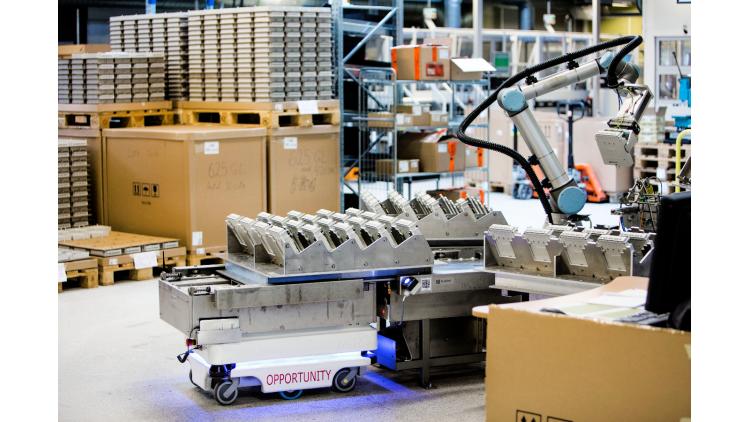
The next row shows mobile robots. These typically have the same local movements as stationary robots with the additional capability of movement. The first robot is the InSight robot which was deployed on Mars in November, 2018.
 |
 |
 |